

Kotlin ranges are created with rangeTo() function, or simply using.
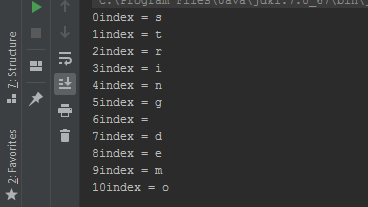
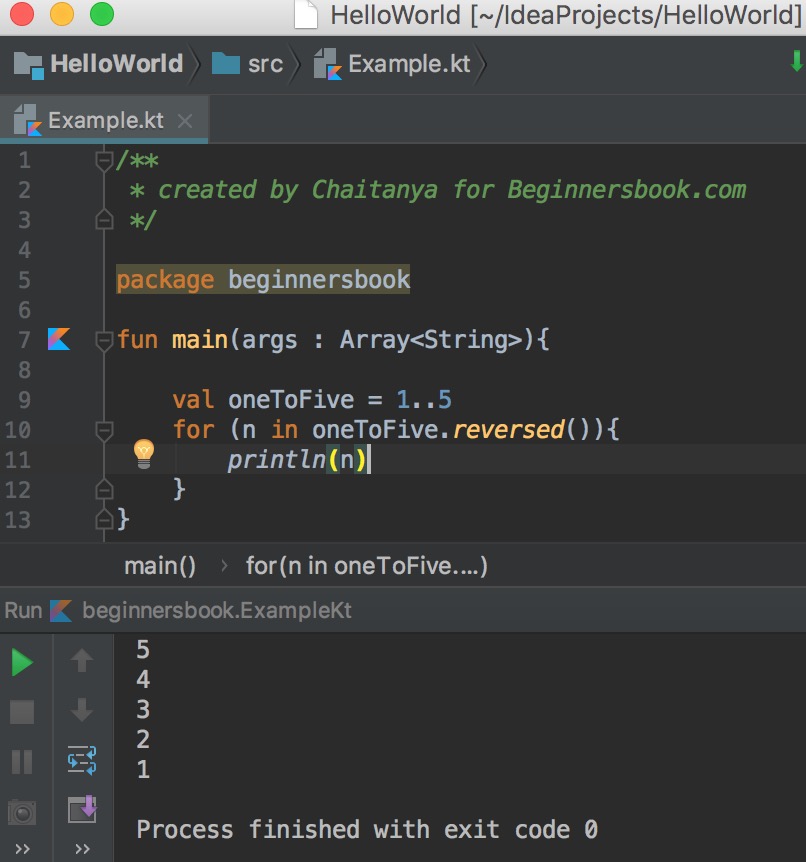
When the operands a and b are statically known to be Float or Double or their nullable counterparts (the type is declared or inferred or is a result of a smart cast), the operations on the numbers and the range that they form follow the IEEE 754 Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic. Kotlin range is defined by its two endpoint values which are both included in the range. Range instantiation and range checks: a.b, x in a.b, x !in a.b The operations on floating-point numbers discussed in this section are: We can use first, last and step properties of a range to find the first, the last value or the step of a range.Here is the complete list of bitwise operations: The function until() can be used to create a range but it will skip the last element given. The function reversed() can be used to reverse the values of a range. Ranges can be created for characters like we have created them for integer values. Let's have a look at the following example: Example We can use step() function to define the distance between the values of the range. If we want to define a backward range we can use the downTo operator: Example You can use Kotlin's slice function to get a part of the list by passing the range of indices. So the above code can be re-written using. Bitwise operations are represented by functions that can be called in infix form. A for loop over a range or an array is compiled to an index-based loop that does not create an iterator object. They operate on the binary level directly with bits of the numbers' representation. The rangeTo() is often called in its operator form. Kotlin provides a set of bitwise operations on integer numbers. When you run the above Kotlin program, it will generate the following output: To create a Kotlin range we call rangeTo() function on the range start value and provide the end value as an argument. Exampleġ.10 // Range of integers starting from 1 to 10Ī.z // Range of characters starting from a to zĪ.Z // Range of capital characters starting from A to Zīoth the ends of the range are always included in the range which means that the 1.4 expression corresponds to the values 1,2,3 and 4. The main operation on ranges is contains, which is usually used in the form of in and !in operators.
Kotlin ranges are created with rangeTo() function, or simply using downTo or (.) operators. According to the documentation for ranges: Floating point numbers ( Double, Float) do not define their rangeTo operator, and the one provided by the standard library for generic Comparable types is used instead: public operator funKotlin range is defined by its two endpoint values which are both included in the range. Its possible to iterate through a range using for loop because ranges provides an iterator.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
